Question
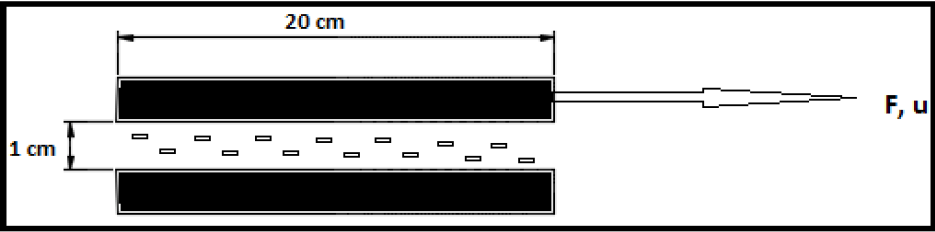
What will be the velocity in m/s of flow at a point 0.5 cm below the lower surface of the upper plate if linear velocity profile is assumed for the flow?
a.
1.25
b.
2.5
c.
12.5
d.
0.25
Posted under Fluid Mechanics
Interact with the Community - Share Your Thoughts
Uncertain About the Answer? Seek Clarification Here.
Understand the Explanation? Include it Here.
Q. The space between two plates (20cm*20cm*1cm), 1 cm apart, is filled with a liquid of viscosity 1 Poise. The upper plate is dragged to the right with a force of 5N keeping the lower...
Similar Questions
Explore Relevant Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q. Cavitation is more pronounced in rough pipes than smooth surfaced pipes.
View solution
Q. For liquid fluids will capillarity rise (or fall) increase or decrease with rise in temperature.
View solution
Q. Capillarity fall is reduced if we take the appartus (capillary tube immersed in fluid having acute angle of contact) considerable distance inside the earth( i.e below the earth crust).
View solution
Q. If a fluid of certain surface tension and diameter is used to create a soap bubble and a liquid jet. Which of the two, bubble or liquid jet, will have greater pressure difference on the inside and outside.
View solution
Q. The surface tension of fluid in contact with air at 25℃ is 0.51N/m. The pressure inside a droplet is to be 0.05 N/cm² greater than outside pressure. Determine the diameter of the droplet of water.
View solution
Q. Will capillary rise occur and if it occurs what will be capillary rise if glass capillarity tube is immersed in water and experiment is carried out by astronauts in space.
View solution
Q. Find the capillarity rise or fall if a capillary tube of diameter .03m is immersed in hypothetical fluid with specific gravity 6.5, surface tension 0.25 N/m and angle of contact 147°.
View solution
Q. An oil of vicosity 7 poise is used for lubrication between shaft and sleeve. The diameter of shaft is 0.6 m and it rotates is 360 rpm. Calculate the power lost in oil for a sleeve length of 160mm. The thickness of oil film is 1.0mm.
View solution
Q. Determine the minimum size of glass tube that can be used to measure water level if the capillary rise in the tube is restricted to 5mm. Consider surface tension of water in contact with air as 0.073 N/m.
View solution
Q. Calculate the magnitude of capillary effect in millimeters in a glass tube of 7mm diameter, when immersed in mercury. The temperature of the liquid is 25℃ and the values of surface tension of mercury at 25℃ is 0.51 N/m. The angle of contact for mercury is 130°.
View solution
Q. What is the variation of cp, cv and k in case of gases when the temperature increases?
View solution
Q. Determine the compressibility of an incompressible fluid, if the pressure of the fluid is changed from 70 N/m² to 130 N/m². The volume of the liquid changes by 0.15 percent.
View solution
Q. A cylinder of 0.8 m³ in volume contains superheated steam at 70℃ and 0.4 N/m² absolute pressure. The superheated steam is compressed to 0.3 . Find pressure and temperature.
View solution
Q. A gas weighs 16 N/m³ at 30℃ and at an absolute pressure of 0.35 N/mm². Determine the gas constant.
View solution
Q. Calculate the pressure exerted by 9 kg of air at a temperature of 20℃ if the volume is 0.8m³. Assuming ideal gas laws are applicable.
View solution
Q. The value of gas constant is same for all the gases.
View solution
Q. If for same temperature and pressure change, the value of bulk modulus is compared for isothermal process and adiabatic process, which one would be higher?
View solution
Q. If the fluid is incompressible, do thermodynamic properties play an important role in its behaviour at varying temperature and pressure?
View solution
Q. For a compressible fluid, if there is no change in specific volume at constant temperature, what type of process it is?
View solution
Q. If there is no exchange of heat between system and surrounding where system comprises of a compressible fluid but the heat is generated due to friction, the process is an adiabatic.
View solution
Recommended Subjects
Are you eager to expand your knowledge beyond Fluid Mechanics? We've handpicked a range of related categories that you might find intriguing.
Click on the categories below to discover a wealth of MCQs and enrich your understanding of various subjects. Happy exploring!








