Question
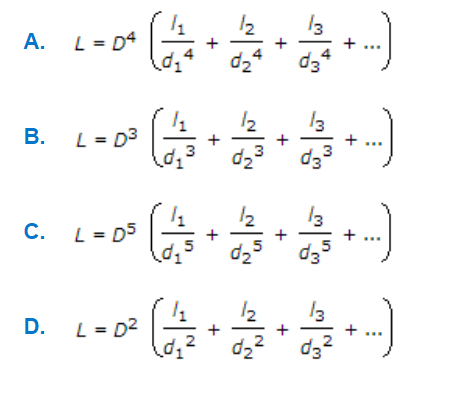
a.
A
b.
B
c.
C
d.
D
Posted under Civil Engineering
Interact with the Community - Share Your Thoughts
Uncertain About the Answer? Seek Clarification Here.
Understand the Explanation? Include it Here.
Q. A pipe consisting of several pipes of varying diameters and lengths, may be replaced by an equivalent pipe of diameter D of length
Similar Questions
Explore Relevant Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q. The following Empirical formula for discharge over large rectangular weirs, is known as
View solution
Q. The diameter (d) of a nozzle fixed at the end of a pipe (diameter D, length L) for maximum energy, is
View solution
Q. The most familiar form of Bernoulli's equation, is
View solution
Q. The mouth piece shown in the below figure is generally known as
View solution
Q. If S is the length of the crest, H is the height of water source of a weir whose length is L and discharge is Q m³/sec, the velocity of approach Vd is
View solution
Q. If u, v, w are the components of the velocity v of a moving particle, then the following equation represents
View solution
Q. The terminal velocity (v) of a sphere of radius r and specific weight W, which travels vertically downwards in a liquid of viscosity μ and specific weight W, is
View solution
Q. Hydraulic gradient is equal to difference in water surfaces
View solution
Q. The valve closure is said to be sudden if
View solution
Q. If Re is the Reynolds's number, the coefficient of friction for laminar flow is
View solution
Q. The length of pipe is L, velocity of flow of a liquid in the pipe is V. If t is the time in second required to close the valve, the head of pressure
View solution
Q. Kinematic viscosity of liquids by following equation is determined by :
View solution
Q. A cylinder 3 m in diameter and 4 m long retains water one side as shown in the below figure. If the weight of the cylinder is 2000 kgf, the vertical reaction at A is
View solution
Q. In the following Newton's viscosity equation, the coefficient (μ) is known as coefficient of
View solution
Q. Which one of the following equation is applicable to unsteady flow in open channels :
View solution
Q. Dimensions of the dynamic viscosity (μ) are
View solution
Q. For pipes not running full, the hydraulic mean depth is given by
View solution
Q. The following equation for the viscosity, is suggested
View solution
Q. The ratio of time for completely emptying the hemispherical tank and circular horizontal tank of equal radii both fitted with similar orifices at their bottoms is :
View solution
Q. To replace a pipe of diameter D by n parallel pipes of diameter d, the formula is
View solution
Recommended Subjects
Are you eager to expand your knowledge beyond Civil Engineering? We've handpicked a range of related categories that you might find intriguing.
Click on the categories below to discover a wealth of MCQs and enrich your understanding of various subjects. Happy exploring!








