Question
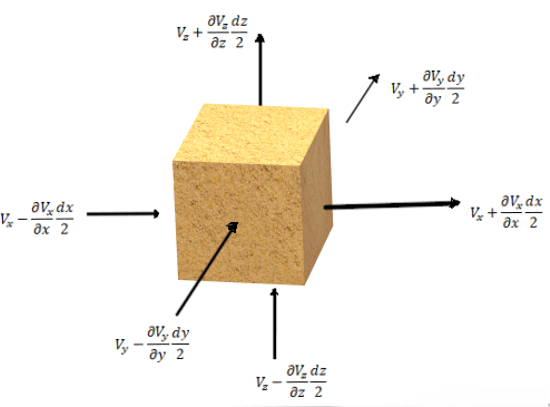
a.
\(q_{out}=(V_x+\frac{∂V_x}{∂x} \frac{dx}{2})dydz+(V_y+\frac{∂V_y}{∂y} \frac{dy}{2})dxdz+(V_z+\frac{∂V_z}{∂z} \frac{dz}{2})dxdy\)
b.
\(q_{out}=(V_x+\frac{∂V_x}{∂x} \frac{dx}{2})dydz-(V_z+\frac{∂V_z}{∂z} \frac{dz}{2})dxdy\)
c.
\(q_{out}=(V_x-\frac{∂V_x}{∂x} \frac{dx}{2})dydz\)
d.
\(q_{out}=(V_x-\frac{∂V_x}{∂x} \frac{dx}{2})dydz-(V_y-\frac{∂V_y}{∂y} \frac{dy}{2})dxdz+(V_z-\frac{∂V_z}{∂z} \frac{dz}{2})dxdy\)
Posted under Geotechnical Engineering
Interact with the Community - Share Your Thoughts
Uncertain About the Answer? Seek Clarification Here.
Understand the Explanation? Include it Here.
Q. Considering a parallelepiped for three dimensional consolidation, the volume of water flowing out of parallelepiped is ______________
Similar Questions
Explore Relevant Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q. The volume of water squeezed out from the parallelepiped is _______________
View solution
Q. The diagram shows a soil profile with following properties:
Sand layer: γsat=20.86 kN/m³
Clay layer: W=38%, Cc=0.26, G=2.72
Find the effective pressure in sand layer.
View solution
Q. The diagram shows a soil profile with following properties:
Sand layer: γsat=20.86 kN/m³
Clay layer: W=38%, Cc=0.26, G=2.72, Z=2m
Find the effective pressure in clay layer.
View solution
Q. The diagram shows a soil profile with following properties:
Sand layer: γsat=20.86 kN/m³
Clay layer: W=38%, Cc=0.26, G=2.72
Find the settlement of the clay layer.
View solution
Q. The decrease in the volume of soil mass under stress is known as __________
View solution
Q. The property of soil mass pertaining to its susceptibility to decrease in volume under pressure is ____________
View solution
Q. Every process involving a decrease in the water content of a saturated soil without replacement of water by air is called _________
View solution
Q. When stress is applied to soil mass, the elastic deformation of solid particles is ____________
View solution
Q. The compression resulting from a long term static load and consequent escape of pore water is _____________
View solution
Q. If increases in the water content due to an increase in the volume of voids is known as _________
View solution
Q. Compression of soil, under short duration of moving or vibratory loads is _________
View solution
Q. Slow vertical deformation occurs when a compressive load is applied to a laterally confined layer of sand.
View solution
Q. The compressibility of clays may also be caused by the following factor.
View solution
Q. The mechanics of consolidation was demonstrated by ___________
View solution
Q. Excess pore pressure is also known as ___________
View solution
Q. In fluid flow calculations, water is considered as incompressible.
View solution
Q. The delay caused in consolidation by the slow drainage of water out of a saturated soil mass is called as __________
View solution
Q. The reduction in volume of soil which is due to squeezing out of water from the voids is __________
View solution
Q. After the hydrostatic pressure is reduced to zero, some compression of soil takes place by the process of _________
View solution
Q. Secondary consolidation is also known as __________
View solution
Recommended Subjects
Are you eager to expand your knowledge beyond Geotechnical Engineering? We've handpicked a range of related categories that you might find intriguing.
Click on the categories below to discover a wealth of MCQs and enrich your understanding of various subjects. Happy exploring!








