Question
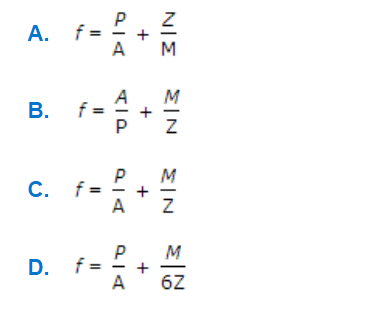
a.
A
b.
B
c.
C
d.
D
Posted under Civil Engineering
Interact with the Community - Share Your Thoughts
Uncertain About the Answer? Seek Clarification Here.
Understand the Explanation? Include it Here.
Q. P is the prestressed force applied to the tendon of a rectangular prestressed beam whose area of cross section is A and sectional modulus is Z. The maximum stress f in the beam,...
Similar Questions
Explore Relevant Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q. If d is the diameter of a bar, ft is allowable tensile stress and fb, is allowable bond stress, the bond length is given b
View solution
Q. If Md and Mt are the maximum bending moments due to dead load and live load respectively and F is the total effective pressure, for a balanced design of a prestreseed concrete beam of steel, is
View solution
Q. If p1 and P2 are effective lateral loadings at the bottom and top exerted by a level earth subjected to a superload on the vertical face of height h of a retaining wall, the horizontal pressure p per unit length of the wall, is
View solution
Q. The modular ratio m of a concrete whose permissible compressive stress is C, may be obtained from the equation.
View solution
Q. If permissible compressive stress in concrete is 50 kg/cm², tensile stress in steel is 1400 kg/cm² and modular ratio is 18, the depth d of the beam, is
View solution
Q. Long and short spans of a two way slab are ly and lx and load on the slab acting on strips parallel to lx and ly be wx and wy respectively. According to Rankine Grashoff theory
View solution
Q. If p is the net upward pressure on a square footing of side b for a square column of side a, the maximum bending moment is given by
View solution
Q. If the tendon is placed at an eccentricity e below the centroidal axis of the lon-gitudial axis of a rectangular beam (sectional modulus Z and stressed load P in tendon) the stress at the extreme top edge
View solution
Q. If Ac, Asc and A are areas of concrete, longitudinal steel and section of a R.C.C. column and m and σc are the modular ratio and maximum stress in the configuration of concrete, the strength of column is
View solution
Q. If W is the load on a circular slab of radius R, the maximum radial moment at the centre of the slab, is
View solution
Q. A pile weighing W1 kg penetrates S metres with its last blow. If W2 is the weight of the hammer having a drop of H metres, the pile can carry a maximum external load
View solution
Q. If W is the uniformly distributed load on a circular slab of radius R fixed at its ends, the maximum positive radial moment at its centre, is
View solution
Q. If p1 and p2 are mutually perpendicular principal stresses acting on a soil mass, the normal stress on any plane inclined at angle θ° to the principal plane carrying the principal stress p1, is :
View solution
Q. If the neutral axis of a T-beam is below the slab, the relationship between the flange width B, depth of neutral axis n, thickness of the slab ds, effective depth of the beam d, gross area of tensile steel At and the modular ratio m may be stated as
View solution
Q. If q is the punching shear resistance per unit area a, is the side of a square footing for a column of side b, carrying a weight W including the weight of the footing, the depth (D) of the footing from punching shear consideration, is
View solution
Q. Based on punching shear consideration, the overall depth of a combined footing under a column A, is
View solution
Q. If the ratio of long and short spans of a two way slab with corners held down is r, the actual reduction of B.M. is given by
View solution
Q. If the length of a combined footing for two columns l metres apart is L and the projection on the left side of the exterior column is x, then the projection y on the right side of the exterior column, in order to have a uniformly distributed load, is (where x is the distance of centre of gravity of column loads).
View solution
Q. If the maximum dip of a parabolic tendon carrying tension P is h and the effective length of the prestressed beam is L, the upward uniform pressure will be
View solution
Q. Total pressure on the vertical face of a retaining wall of height h per unit run exerted by the retained earth weighing w per unit volume, is
View solution
Recommended Subjects
Are you eager to expand your knowledge beyond Civil Engineering? We've handpicked a range of related categories that you might find intriguing.
Click on the categories below to discover a wealth of MCQs and enrich your understanding of various subjects. Happy exploring!








