Question
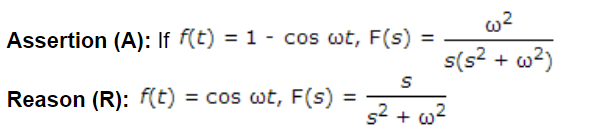
a.
Both A and R are correct and R is correct explanation of A
b.
Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A
c.
A is true, R is false
d.
A is false, R is true
Posted under Electronics and Communication Engineering
Interact with the Community - Share Your Thoughts
Uncertain About the Answer? Seek Clarification Here.
Understand the Explanation? Include it Here.
Q. Consider the following two statements :
Similar Questions
Explore Relevant Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q. A rectangular pulse train s(t) is shown in figure is convolved with the signal cos²(4π x 10³t). The convolved signal will be a
View solution
Q. The z-transform of sequence n x x[n] is
View solution
Q. The inverse Laplace transform of
View solution
Q. The function f(t) in the given figure will have its Laplace transform as
View solution
Q. The joint probability function of two discrete random variable X and Y is given by following equation. Then E(X) =
View solution
Q. The effective value of the waveform in the given figure is
View solution
Q. Which one of following is a static system?
View solution
Q. The Laplace transform of unit ramp function starting at t = a is
View solution
Q. If i(t) is a time varying current, then following is
View solution
Q. For the discrete time system of the given figure
View solution
Q. The following signal is
View solution
Q. If H(z) is given by following equation, the poles of H(z) are at
View solution
Q. The function x(t) is shown in the given figure. Even and odd parts of a unit step function ∪ (t) are respectively,
View solution
Q. Fourier transform of -jt f(t) is
View solution
Q. DTFT (Discrete time Fourier transform) of x[n] = aⁿ∪[n] for -1 < a < + 1.
View solution
Q. The given figure shows a discrete time system consisting of a unit delay system, a multiplier and a summer, such that y(k) = x(k - 1) + 0.5 x(k). This system
View solution
Q. The joint probability function of two discrete random variable X and Y is given below.
Then E(y) is
View solution
Q. The joint probability function of two discrete random variable X and Y is given below.
Variance σ² will be
[Hint: σ² = E(X²) - μ² ⇒ E(X²) - (E(X))²]
View solution
Q. A probability density function is given by p(x) = Ke^(-x²/2) for -∞ < x < ∞ , The value of K should be
View solution
Q. The Laplace transform of f(t) is
View solution
Recommended Subjects
Are you eager to expand your knowledge beyond Electronics and Communication Engineering? We've handpicked a range of related categories that you might find intriguing.
Click on the categories below to discover a wealth of MCQs and enrich your understanding of various subjects. Happy exploring!








