Question
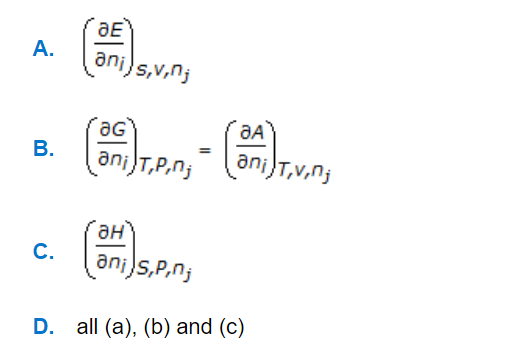
a.
A
b.
B
c.
C
d.
D
Posted under Basic Chemical Engineering
Interact with the Community - Share Your Thoughts
Uncertain About the Answer? Seek Clarification Here.
Understand the Explanation? Include it Here.
Q. The chemical potential of a component (μi) of a phase is the amount by which its capacity for doing all work, barring work of expansion is increased per unit amount of substance...
Similar Questions
Explore Relevant Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q. Co-efficient of performance for a reversed Carnot cycle working between temperatures T₁ and T₂ (T₁ > T₂) is
View solution
Q. Following is the mathematical expression for
View solution
Q. What is the value of maximum COP in case of absorption refrigeration, if refrigeration provided is at temperature, Tʀ(where, T₁ and T₂ are source & surrounding temperatures respectively.)?
View solution
Q. Following is the mathematical expression for
View solution
Q. Which of the following diagrams does not represent an Otto cycle ?
View solution
Q. Following is the mathematical expression for
View solution
Q. An ideal gas is taken around the cycle ABCA as shown in P-V diagram below. The work done by the gas during the cycle is equal to
View solution
Q. The Maxwell relation derived from the differential expression for the Helmholtz free energy (dA) is
View solution
Q. Gibbs free energy (G) is represented by, G = H - TS, whereas Helmholtz free energy, (A) is given by, A = E - TS. Which of the following is the Gibbs-Helmholtz equation
View solution
Q. Which of the following is clausius-Clayperon equation for vaporisation of an ideal gas under the condition that the molar volume of liquid is negligible compared to that of the vapor ?
View solution
Q. Which of the following is not a unit of the equilibrium constant Kp? (where, Δx = number of moles of products number of moles of reactants)
View solution
Q. Which is not constant for an ideal gas ?
View solution
Q. Following is the mathematical expression for
View solution
Q. The ratio of equilibrium constants (Kp₂/Kp₁) at two different temperatures is given by
View solution
Q. Consider the process A & B shown in the figure given below. In this case, it is possible that
View solution
Q. Joule-Thomson co-efficient which is defined by equation given below, changes sign at a temperature known as inversion temperature. The value of Joule-Thomson co-efficient at inversion temperature is
View solution
Q. The equation relating E, P, V and T which is true for all substances under all conditions is given by following equation .This equation is called the
View solution
Q. Cᵥ is given by
View solution
Q. The root mean square speed of molecules of a gas is equal to (where, m = mass of the molecule K = Boltzman's constant, T = absolute temperature)
View solution
Q. Efficiency of a Carnot engine working between temperatures T₁ and T₂ (T₁ < T₂) is
View solution
Recommended Subjects
Are you eager to expand your knowledge beyond Basic Chemical Engineering? We've handpicked a range of related categories that you might find intriguing.
Click on the categories below to discover a wealth of MCQs and enrich your understanding of various subjects. Happy exploring!








