Question
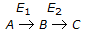
a.
increase of temperature.
b.
decrease of temperature.
c.
increase in initial concentration of A.
d.
decrease in initial concentration of A.
Posted under Basic Chemical Engineering
Interact with the Community - Share Your Thoughts
Uncertain About the Answer? Seek Clarification Here.
Understand the Explanation? Include it Here.
Q. In a consecutive reaction system given below, when E₁ is much greater than E₂, the yield of B increases with the
Similar Questions
Explore Relevant Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q. For the irreversible elementary reactions in parallel like given below, the rate of disappearance of 'X' is equal to
View solution
Q. For an isothermal variable volume batch reactor, the following relation is applicable for a first order irreversible reaction.
View solution
Q. Effective diffusivity (DE) in a catalyst pellet is related to molecular diffusivity (DN) and Knudsen diffusivity (DK) as
View solution
Q. For a vapour phase catalytic reaction (A + B → P) which follows the Ridel mechanism and the reaction step is rate controlling, the rate of reaction is given by (reaction rate is irreversible, product also absorbs).
View solution
Q. For a series of reactions given below, having k1 << k2, the reaction system can be approximated as
View solution
Q. What is the Thiele modulus of the solid catalysed first order reaction given below, if the pore diffusion offers negligible resistance to reaction ?
View solution
Q. The exit age distribution of a fluid leaving a vessel (denoted by E) is used to study the extent of non-ideal flow in the vessel. The value of following integral is
View solution
Q. Three plug flow reactors (PFR's) of 4, 5 & 6 m³ volumes are arranged in two branches as shown below in the figure.
If the total feed rate is 300 tons/hr, then for the same conversion in each branch, the feed rate through branch II should be __________ tons/hr.
View solution
Q. A first order gaseous phase reaction is catalysed by a non-porous solid. The kinetic rate constant and the external mass transfer co-efficients are k and kg respectively. The effective rate constant (kₑff) is given by
View solution
Q. If Cᴀ is the quantity of reactants initially present, the quantity left after 'n' half periods will be equal to
View solution
Q. The rate controlling step for the heterogeneous irreversible catalytic reaction A(g) + B(g) → C(g) is the surface reaction of absorbed A with absorbed B to give adsorbed C. The rate expression for this reaction can then be written as (where, Kᴀ, Kʙ and Kc are the equilibrium constants and is the rate constant of the rate controlling step.)
View solution
Q. The conversion for a second order, irreversible reaction (constant volume) given below, in batch mode is given by
View solution
Q. A first order homogeneous reaction of the type X → Y → Z (consecutive reaction) is carried out in a CSTR. Which of the following curves respectively show the variation of the concentration of X, Y and Z with time?
View solution
Q. In a chemical reaction given below , it is observed that the
(i) rate of formation of 'P' is doubled on doubling the concentration of 'X'.
(ii) rate of formation of 'P' is quadrupled on doubling the concentration of 'Y'.
(iii) doubling the concentration of 'Z' does not affect the rate of formation of 'P'.
What is the order of the above chemical reaction?
View solution
Q. Transition state theory relates the above quantities as
View solution
Q. For a first order reaction carried out in a plug flow reactor, the space time is
View solution
Q. Second order consecutive irreversible reactions given below were carried out in a constant volume isothermal batch reactor with different initial feed compositions. Reactor temperature was same in all the cases. In experiments where the ratio of concentration of B to that of A in the initial feed was less than 0.5, the concentration of B increased first, reached a maximum and then declined with time. However, for all experiments where this concentration ratio was 0.5 or above, concentration of B decreased monotonically with time right from the beginning. What is the ratio of the two rate constants (k₁/k₂)?
View solution
Q. A consecutive reaction given below, is characterised by
View solution
Q. Pick the WRONG design guideline for a reactor in which the reactions, A → R (desired) and A → S (undesired) are to take place. The ratio of the reaction rates is as given below .
View solution
Q. In case of a consecutive unimolecular type first order reaction given below, the concentration of component __________ increases continuously with time.
View solution
Recommended Subjects
Are you eager to expand your knowledge beyond Basic Chemical Engineering? We've handpicked a range of related categories that you might find intriguing.
Click on the categories below to discover a wealth of MCQs and enrich your understanding of various subjects. Happy exploring!








