Question
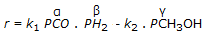
a.
α = 1, β = 1, γ =1
b.
α = 1, β = 2, γ = 1
c.
α = 1/3, β = 2/3, γ = 1/3
d.
α = 1/2, β = 1, γ = 1/2
Posted under Basic Chemical Engineering
Interact with the Community - Share Your Thoughts
Uncertain About the Answer? Seek Clarification Here.
Understand the Explanation? Include it Here.
Q. The rate expression for the gaseous phase reaction, CO + 2H₂ ↔ CH₃OH, is given below. Which of the following is not possible ?
Similar Questions
Explore Relevant Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q. The exit age distribution curve E(t) for an ideal CSTR with the average residence time, τ, is given by
View solution
Q. A second order liquid phase reaction, A → B, is carried out in a mixed flow reactor operated in semi batch mode (no exit stream). The reactant A at concentration CAF is fed to the reactor at a volumetric flow rate of F. The volume of the reacting mixture is V and the density of the liquid mixture is constant. The mass balance for A is
View solution
Q. The following half life data are available for the irreversible liquid phase reaction A → products. The overall order of reaction is
View solution
Q. A non-catalytic chemical reaction of the following type is called a __________ reaction.
View solution
Q. The reaction rate constants at two different temperature T₁ and T₂ are related by
View solution
Q. What is the order of chemical reaction given below , if it is found that the reaction rate doubles on doubling the concentration of B and also the reaction rate doubles when the concentrations of both A & B were doubled and quandrupled when the concentrations of both B & C were doubled ?
View solution
Q. If n = overall order of a chemical reaction, a = initial concentration of reactant, t = time required to complete a definite fraction of the reaction. Then pick out the correct relationship.
View solution
Q. The order of the chemical reaction given below, whose rate equation is given as -rᴀ = KCᴀ². Cʙ is
View solution
Q. With increase in K₂/K₁ in case of a unimolecular type elementary reactions given below, the fractional yield of 'R' in mixed reactor (for a given conversion of 'A')
View solution
Q. Collision theory gives the rate constant for bimolecular reaction as
View solution
Q. The temperature dependence of reaction rate constant (K) by Arhenius law is given by
View solution
Q. For a __________ order chemical reaction given below, the fractional conversion of reactant 'A' is proportional to time.
View solution
Q. Consider a reversible exothermic reaction in a plug flow reactor. The maximum and minimum permissible temperatures are Tₘₐₓ and Tₘᵢₙ respectively. Which of the following temperature (T) profiles will require the shortest residence time to achieve the desired conversion.
View solution
Q. Rate constant 'k' and absolute temperature 'T' are related by collision theory (for bimolecular) as
View solution
Q. The residence time distribution of an ideal CSTR is
View solution
Q. In case of unimolecular type elementary reaction given below, plug flow reactor as compared to mixed reactor is
View solution
Q. The first order series reaction given below, is conducted in a batch reactor. The initial concentrations of A, B and C (Cᴀ₀, Cʙ₀, Cc₀ respectively) are all non-zero. The variation of Cʙ with reaction time will not show a maximum, if
View solution
Q. Effectiveness factor (E) of a catalyst pellet is defined as below. Effectiveness factor for a first order reaction is given by (where, T = Thiele modulus)
View solution
Q. The mean conversion in the exit stream, for a second order, liquid phase reaction in a non-ideal flow reactor is given by
View solution
Q. Concentration of the limiting reactant (with initial concentration of a moles/litre) after time t is (a-x). Then 't' for a first order reaction is given by
View solution
Recommended Subjects
Are you eager to expand your knowledge beyond Basic Chemical Engineering? We've handpicked a range of related categories that you might find intriguing.
Click on the categories below to discover a wealth of MCQs and enrich your understanding of various subjects. Happy exploring!








