Question
a.
σ’=0, u̅ =12
b.
σ’=10+∆σ’, u̅ =2-∆σ’
c.
σ’=10, u̅ =2
d.
σ’=12, u̅ =0
Posted under Geotechnical Engineering
Interact with the Community - Share Your Thoughts
Uncertain About the Answer? Seek Clarification Here.
Understand the Explanation? Include it Here.
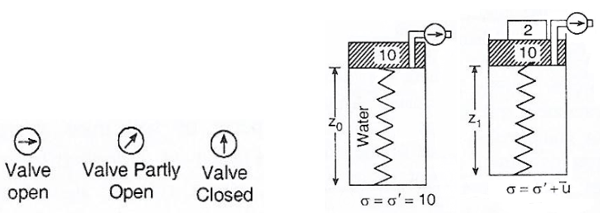
Q. In the spring analogy of consolidation, cylinder is filled with water up to bottom of piston and spring carries 10 units of load. If external two units of load is applied and the...
Similar Questions
Explore Relevant Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q. In the spring analogy of consolidation, cylinder is filled with water up to bottom of piston and spring carries 10 units of load. If external two units of load is applied and the valve is opened, then the effective pressure σ’ and hydrodynamic pressure u̅ is given by ___________
View solution
Q. In finding pre-consolidation pressure, initial portion of curve resembles ___________
View solution
Q. In determination of one-dimensional consolidation as shown in the figure, the line CD represents ___________
View solution
Q. In determination of one-dimensional consolidation as shown in the figure, the line AB represents ___________
View solution
Q. If v is velocity at the entry of the soil element of size dx, dz and width dy as shown in the figure. The quantity of water entering the element is ___________
View solution
Q. If v is velocity at the entry of the soil element of size dx, dz and width dy as shown in the figure. The quantity of water leaving the element is ___________
View solution
Q. If v is velocity at the entry of the soil element of size dx, dz and width dy as shown in the figure. The net quantity of water squeezed out of the element per unit time is ___________
View solution
Q. In the graph, point Rc represents ________
View solution
Q. The graph is plotted with the procedure of square root of time fitting method. The line B is drawn that its abscissa at every point is ______ times that of line A.
View solution
Q. The primary consolidation is from _____________
View solution
Q. The secondary consolidation is from __________
View solution
Q. Considering a parallelepiped for three dimensional consolidation, the volume of water flowing into parallelepiped is __________
View solution
Q. Considering a parallelepiped for three dimensional consolidation, the volume of water flowing out of parallelepiped is ______________
View solution
Q. The volume of water squeezed out from the parallelepiped is _______________
View solution
Q. The diagram shows a soil profile with following properties:
Sand layer: γsat=20.86 kN/m³
Clay layer: W=38%, Cc=0.26, G=2.72
Find the effective pressure in sand layer.
View solution
Q. The diagram shows a soil profile with following properties:
Sand layer: γsat=20.86 kN/m³
Clay layer: W=38%, Cc=0.26, G=2.72, Z=2m
Find the effective pressure in clay layer.
View solution
Q. The diagram shows a soil profile with following properties:
Sand layer: γsat=20.86 kN/m³
Clay layer: W=38%, Cc=0.26, G=2.72
Find the settlement of the clay layer.
View solution
Q. The decrease in the volume of soil mass under stress is known as __________
View solution
Q. The property of soil mass pertaining to its susceptibility to decrease in volume under pressure is ____________
View solution
Q. Every process involving a decrease in the water content of a saturated soil without replacement of water by air is called _________
View solution
Recommended Subjects
Are you eager to expand your knowledge beyond Geotechnical Engineering? We've handpicked a range of related categories that you might find intriguing.
Click on the categories below to discover a wealth of MCQs and enrich your understanding of various subjects. Happy exploring!








