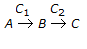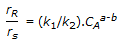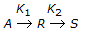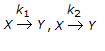Chemical Reaction Engineering MCQs
Welcome to our comprehensive collection of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) on Chemical Reaction Engineering, a fundamental topic in the field of Basic Chemical Engineering. Whether you're preparing for competitive exams, honing your problem-solving skills, or simply looking to enhance your abilities in this field, our Chemical Reaction Engineering MCQs are designed to help you grasp the core concepts and excel in solving problems.
In this section, you'll find a wide range of Chemical Reaction Engineering mcq questions that explore various aspects of Chemical Reaction Engineering problems. Each MCQ is crafted to challenge your understanding of Chemical Reaction Engineering principles, enabling you to refine your problem-solving techniques. Whether you're a student aiming to ace Basic Chemical Engineering tests, a job seeker preparing for interviews, or someone simply interested in sharpening their skills, our Chemical Reaction Engineering MCQs are your pathway to success in mastering this essential Basic Chemical Engineering topic.
Note: Each of the following question comes with multiple answer choices. Select the most appropriate option and test your understanding of Chemical Reaction Engineering. You can click on an option to test your knowledge before viewing the solution for a MCQ. Happy learning!
So, are you ready to put your Chemical Reaction Engineering knowledge to the test? Let's get started with our carefully curated MCQs!
Chemical Reaction Engineering MCQs | Page 5 of 50
Discover more Topics under Basic Chemical Engineering