Question
a.
– 1052.4 degree celsius
b.
– 2052.4 degree celsius
c.
– 3052.4 degree celsius
d.
– 4052.4 degree celsius
Posted under Heat Transfer
Interact with the Community - Share Your Thoughts
Uncertain About the Answer? Seek Clarification Here.
Understand the Explanation? Include it Here.
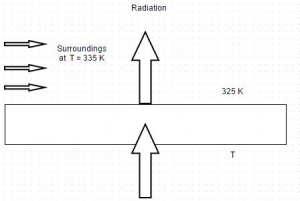
Q. The diagram shows heat conduction through a plane wall. The surface temperature is 475 K and it radiates heat to the surroundings at 335 K. If thermal conductivity of the material...
Similar Questions
Explore Relevant Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q. From the concept of kinetic theory, mean travel velocity of the gas molecules is prescribed by the relation
(Where,
G = Universal gas constant
M = Molecular weight of the gas
T = Absolute temperature)
View solution
Q. Low temperature insulation are used when the enclosure is at a temperature lower than the ambient temperature. Which one of the following is not a low temperature insulation?
View solution
Q. The value of Lorenz number in 10¯⁸ W ohms/K² is
View solution
Q. Consider the following parameters
(i) Composition
(ii) Density
(iii) Porosity
(iv) Structure
Then, thermal conductivity of glass wool varies from sample to sample because of variation is
View solution
Q. The thermal conductivity and the electrical conductivity of a metal at absolute temperature are related as
View solution
Q. The relation Ϫ² t =0 is referred to as
View solution
Q. The unit of thermal diffusivity is
View solution
Q. To effect a bond between two metal plates, 2.5 cm and 15 cm thick, heat is uniformly applied through the thinner plate by a radiant heat source. The bonding must be held at 320 K for a short time. When the heat source is adjusted to have a steady value of 43.5 k W/m², a thermocouple installed on the side of the thinner plate next to source indicates a temperature of 345 K. Calculate the temperature gradient for heat conduction through thinner plate. In the diagram, the upper plate is 2.5 cm thick while the lower is 15 cm thick.
View solution
Q. The diffusion equations
Ɏ²t + q g = (1/α) (d t/d r)
Governs the temperature distribution under unsteady heat flow through a homogenous and isotropic material. The Fourier equation follows from this expression when
View solution
Q. The famous Fourier series is named after
View solution
Q. Fourier law of heat conduction is best represented by
View solution
Q. Here are some assumptions that are made for Fourier law. Identify the wrong one
View solution
Q. Consider the following statements:
The Fourier heat conduction equation
Q = -k A d t /d x
Presumes
i) Steady state conditions
ii) Constant value of thermal conductivity
iii) Uniform temperature at the wall surface
iv) One dimensional heat flow
Which of these statements are correct?
View solution
Q. Negative sign in Fourier heat conduction equation indicates
View solution
Q. Transmission of heat i.e. molecular is smallest in case of
View solution
Q. Which one is not the unit of thermal conductivity?
View solution
Q. “Thermal conductivity represents the amount of heat conducted across unit area when a temperature difference of one kelvin”. True or false
View solution
Q. Which of the following is the unit of thermal resistance?
View solution
Q. Thermal conductivity is defined as the heat flow per unit time
View solution
Q. Mark the matter with least value of thermal conductivity
View solution
Recommended Subjects
Are you eager to expand your knowledge beyond Heat Transfer? We've handpicked a range of related categories that you might find intriguing.
Click on the categories below to discover a wealth of MCQs and enrich your understanding of various subjects. Happy exploring!








