Question
a.
A
b.
B
c.
C
d.
D
Posted under Electronics and Communication Engineering
Interact with the Community - Share Your Thoughts
Uncertain About the Answer? Seek Clarification Here.
Understand the Explanation? Include it Here.
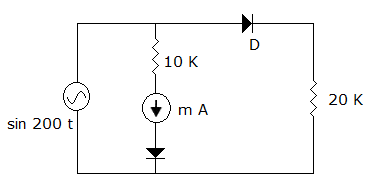
Q. The diode and the moving coil milliammeter of figure are assumed to be ideal. The meter reading is
Similar Questions
Explore Relevant Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q. The V-I characteristic of a semi-conductor diode is shown in figure. From this figure it can be concluded that
View solution
Q. Which of the following expressions may be used to correctly describe the temperature (T) variation of the intrinsic carrier density (ni) of a semiconductor?
View solution
Q. Figure represents a
View solution
Q. Figure shows the terminals of a transistor in plastic package TO 18. Then
View solution
Q. The network shown in the figure represents a
View solution
Q. In a junction transistor biased for operation at emitter current 'IE' and collector current 'IC' the transconductance 'gm' is.
View solution
Q. CE saturation resistance of n-p-n transistor is
View solution
Q. Typical values of h parameters at about 1 mA collector current for small signal audio amplifier in CE configuration are :
View solution
Q. R.M.S. value of the waveform shown will be
View solution
Q. For a UJT if
R1 = Resistor from emitter to the base 1
R2 = Resistor from emitter to the base 2 and RBB = R1 + R2,
then the intrinsic stand off ratio (η) is
View solution
Q. The kinetic energy of free electrons in a metal is (where k is de-Broglie wave number of the electrons)
View solution
Q. Ripple factor is
View solution
Q. Figure represents a
View solution
Q. A p-n junction diode has
View solution
Q. Which of the following is true as regards photo emission?
View solution
Q. The power dissipation in a transistor is the product of
View solution
Q. The normal operation of JFET is
View solution
Q. The minority carrier life time and diffusion constant in a semiconductor material are respectively 100 microsecond and 100 cm²/sec. The diffusion length is
View solution
Q. At room temperature the current in an intrinsic semiconductor is due to
View solution
Q. Work function is the maximum energy required by the fastest electron at 0 K to escape from the metal surface.
View solution
Recommended Subjects
Are you eager to expand your knowledge beyond Electronics and Communication Engineering? We've handpicked a range of related categories that you might find intriguing.
Click on the categories below to discover a wealth of MCQs and enrich your understanding of various subjects. Happy exploring!








